The Financial Stability Oversight Council (comprised of an alphabet soup of US financial regulators) has released its 2011 Annual Report.
There are many items of interest in this excellent report; one issue that I find interesting is the regulation of money market funds:
The stable, rounded $1 NAV fosters an expectation that MMF share prices will not fluctuate. However, when shareholders perceive that a fund may suffer losses, each shareholder has an incentive to redeem shares before other shareholders, causing a run on the fund. Such redemptions can accelerate the likelihood of a break-the-buck event to the extent that the fund’s asset sales to meet redemptions significantly depress the market value of the fund’s remaining assets. In such a scenario, the ability of early redeemers to receive the full $1 NAV is essentially subsidized by the losses absorbed by remaining shareholders.
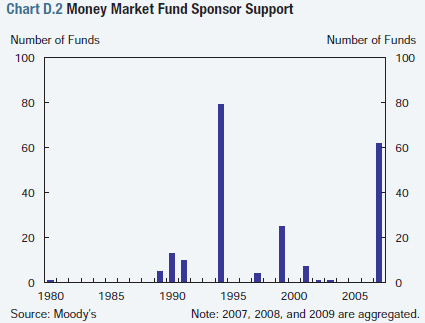
MMFs invest in assets that may lose value, but funds have no formal capital buffers or insurance to absorb loss and maintain their stable NAV. When losses do occur, MMFs have historically relied on discretionary sponsor support to maintain a stable NAV and preserve the franchise value of fund management businesses (Chart D.2). That support may come in the form of capital contributions or the purchase of assets that have lost value, for example.
Sponsors do not commit to support an MMF in advance, however, because an explicit commitment may require the sponsor to consolidate the fund on its balance sheet. Thus, although investors ostensibly bear the risk of an MMF breaking the buck, sponsors have in the past borne that risk themselves, fostering the perceived safety of MMF investments. Moreover, the uncertainty about the availability and sufficiency of such support during crises, and the fact that many MMFs lack deep-pocketed sponsors, contribute to their susceptibility to runs.
Expectation of Government Support
Given the unprecedented government support of MMFs during the crisis in 2008 and 2009, even sophisticated institutional investors and fund managers may have the impression that the government would be ready to support the industry again with the same tools.
…
Although these new rules are a positive first step, the SEC recognizes that they address only some of the features that make MMFs susceptible to runs, and that more should be done to address systemic risks posed by MMFs and their structural vulnerabilities.
The report takes a much more reasonable view of the Flash Crash than did the highly politicized SEC report:
During periods of violent price movements, market liquidity can evaporate as hedging strategies to protect against market risk become strained or directly amplify the price movements. For example, in the October 1987 equity market crash, portfolio insurance programs were designed to sell when prices declined; in fact, they were set to sell at an increasing rate, thereby accelerating the market decline. Similarly, in the flash crash of May 6, 2010, liquidity evaporated and market functioning deteriorated rapidly. Regulators have added circuit breakers in equity markets to mitigate such dynamics (see Section 5.3.4), but this event illustrated the potential fragility of market liquidity, particularly in areas characterized by rapid innovation and change in market behaviors.
The role of exchange traded funds (ETFs) during the flash crash has focused attention on these products. The rapid rise of ETFs has been driven by the attraction of gaining liquid exposure to less liquid asset classes—such as commodities and certain emerging markets—without having to execute trades directly in less liquid markets (Chart E.1). However, the liquidity of ETFs depends heavily on the support of market makers and on market functioning in the underlying asset. The relationship between ETF turnover and market volatility bears further analysis, and regulators must continue to monitor the development of more complex products in both U.S. and foreign-domiciled funds that might heighten liquidity concerns.
One item of great interest to me was developments in the idea that insurance companies should be regulated at the consolidated level – there is not a single mention of this in the report, so for the moment I will assume that this highly desirable reform has been dropped. Instead, the report discusses the new Federal Insurance Office (FIO), which is just another micromanaging job-creation scheme.
[…] 2011 Annual Report of the FSOC has been discussed on PrefBlog. Anyway, back to Schapiro: While floating NAVs would reinforce what money market funds are – an […]