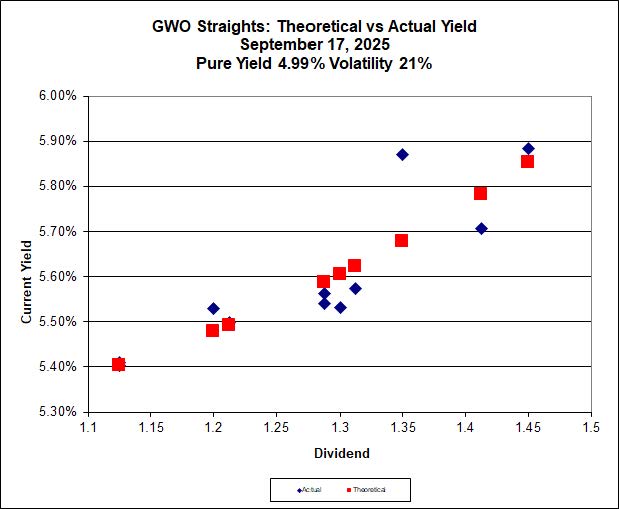
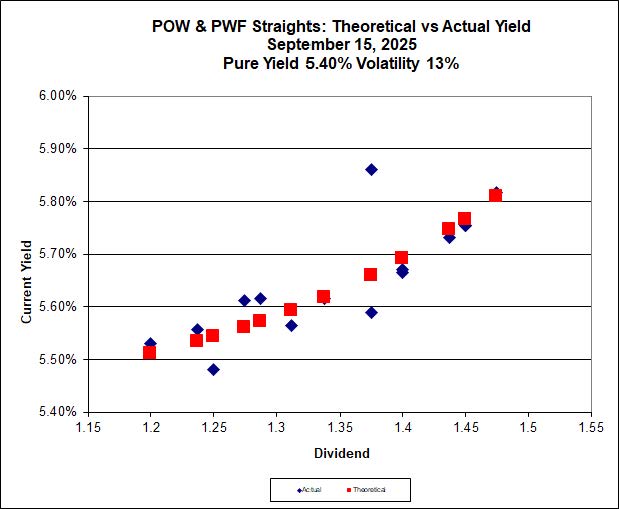
Partners Value Split Corp. has announced (although not yet on their website):
that it has entered into an agreement to sell 5,000,000 Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 14 (the “Series 14 Preferred Shares”) to a syndicate of underwriters led by Scotiabank, BMO Capital Markets, CIBC Capital Markets, RBC Capital Markets and TD Securities Inc. on a bought deal basis.
The Series 14 Preferred Shares will be issued at a price of $25.00 per share, for gross proceeds of $125,000,000. The Series 14 Preferred Shares will carry a fixed coupon of 5.50% and will have a final maturity of June 30, 2030. The Series 14 Preferred Shares have a provisional rating of Pfd-2 from DBRS Limited. The net proceeds of the offering will be used by the Company in connection with the Company’s redemption of its outstanding Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 8 and to pay a special dividend on the Company’s capital shares.
The Company has granted the underwriters an option, exercisable in whole or part prior to closing, to purchase up to an additional 1,000,000 Series 14 Preferred Shares at the same offering price, which, if exercised in full, would increase the gross offering size to $150,000,000. Closing of the offering is expected to occur on or about September 27, 2024.
The Company owns a portfolio consisting of approximately 119 million Class A Limited Voting Shares of Brookfield Corporation and approximately 30 million Class A Limited Voting Shares of Brookfield Asset Management Ltd. (collectively, the “Brookfield Securities”),which are expected to yield quarterly dividends that are sufficient to fund quarterly fixed cumulative preferential dividends for the holders of the Company’s preferred shares and to enable the holders of the Company’s capital shares to participate in any capital appreciation of the Brookfield Securities.
Brookfield Corporation is a leading global investment firm focused on building long-term wealth for institutions and individuals around the world. Brookfield Corporation has three core businesses: alternative asset management, wealth solutions, and its operating businesses which are in renewable power, infrastructure, business and industrial services, and real estate. Brookfield Corporation is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and Toronto Stock Exchange under the symbol BN.
Brookfield Asset Management Ltd. (“BAM”) is a leading global alternative asset manager with approximately US$1 trillion of assets under management across renewable power & transition, infrastructure, private equity, real estate, and credit. BAM’s objective is to generate attractive, long-term risk-adjusted returns for the benefit of its clients and shareholders. BAM is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and Toronto Stock Exchange under the symbol BAM.
Jason Weckwerth, Chief Financial Officer, will be available at (416) 363-9491 to answer any questions regarding the offering.
The prospectus is available at SEDARPlus, but as usual I am not permitted – or able – to post a link to it, because the Canadian Securities Administrators consider this information to be TOP SECRET and not something for investors to worry their pretty little heads about. Anyway, search for
“Partners Value Split Corp. / Partners Value Split Corp. (000016555)
Prospectus (non pricing) supplement (other than ATM) – English.pdf
23 Sep 2024 20:35 EDTSeptember 23 2024 at 20:35:46 Eastern Daylight Time
Ontario
511 KB
Generate URL”
Anyway, from the prospectus:
Quarterly dividends on the Series 14 Preferred Shares will be paid by the Company on or about the 7th day of March, June, September and December in each year. Based on the anticipated closing date of September 27, 2024, the initial dividend (which covers the period from closing to November 30, 2024) is expected to be $0.24486 per Series 14 Preferred Share, and is expected to be paid on or about December 7, 2024 to holders of record on November 22, 2024. The Series 14 Preferred Shares may be surrendered for retraction at any time. The Company will redeem all outstanding Series 14 Preferred Shares on June 30, 2030 (the “Series 14 Redemption Date”) for a cash amount per share equal to the lesser of (i) $25.00 plus any accrued and unpaid dividends and (ii) the Net Asset Value per Unit (as defined herein). See “Details of Offering — Series 14 Preferred Shares” and “Dividend Policy”.
…
The Series 14 Preferred Shares have been provisionally rated Pfd-2 by DBRS Limited (“DBRS”).
…
A holder retracting Series 14 Preferred Shares will receive per Series 14 Preferred Share retracted, as payment for such shares, a number of debentures (the “Series 12 Debentures”) determined by dividing the holder’s aggregate Preferred Share Retraction Price (as defined below) by $25.00, being the principal amount of the Series 12 Debenture.
…
Series 14 Preferred Shares may be redeemed by the Company at any time on or after June 30, 2028 and prior to June 30, 2030 (the “Series 14 Redemption Date”) at a price (the “Series 14 Preferred Share Redemption Price”), which, prior to June 30, 2029 will equal $25.50 per share plus accrued and unpaid dividends and which will decline by $0.50 on June 30, 2029. All Series 14 Preferred Shares outstanding on the Series 14 Redemption Date will be redeemed for a cash amount equal to the lesser of $25.00 plus any accrued and unpaid dividends, and the Net Asset Value per Unit. Notwithstanding the first sentence of this paragraph, the Company may redeem Series 14 Preferred Shares prior to June 30, 2028 for $26.00 per share plus accrued and unpaid dividends if, and will not redeem Series 14 Preferred Shares prior to June 30, 2028 unless: (i) Capital Shares have been retracted; or (ii) there is a take-over bid for the BN Shares and the board of directors of the Company determines that such bid is in the best interest of the holders of the Capital Shares.
…
The Series 14 Preferred Shares will rank prior to the Capital Shares, the Class AAA Preferred Shares and the Junior Preferred Shares and on a pari passu basis with all other Preferred Shares (other than the Class AAA Preferred Shares and the Junior Preferred Shares) with respect to the payment of dividends, distributions upon a redemption, retraction or return of capital and distributions upon a dissolution, liquidation or winding-up of the Company.
…
Holders of the Series 12 Debentures will be entitled to receive quarterly fixed interest payments at a rate of 5.60% per annum. Interest will be paid by the issuer of the Series 12 Debentures (the “Issuer”) quarterly on or about the 7th day of March, June, September and December in each year; provided that the Issuer may, at its option, provided no Event of Default (as defined under “Events of Default”) has occurred and is continuing, elect to defer payment of interest due on any interest payment date until maturity on the condition that, in the event of such an election, no interest, dividends or other distributions will be permitted to be paid in respect of any of the Company’s subordinate classes of securities.
…
The Series 12 Debentures will be direct unsecured obligations of the Issuer and will rank junior to all other unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness incurred by the Issuer and prior to all Preferred Shares and, if issued by the Issuer, the capital shares of such Issuer, with respect to the payment of interest and repayment of the outstanding principal amount.
I have no idea what the ticker might be when these get issued.
Thanks to Assiduous Reader IrateAR for bringing this to my attention!
Update, 2024-9-24:DBRS Provisional Pfd-2 Rating:
DBRS Limited (Morningstar DBRS) assigned a provisional credit rating of Pfd-2 to the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 14 (the Series 14 Preferred Shares) to be issued by Partners Value Split Corp. (the Company) that will rank pari passu with the existing Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 8; the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 9; the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 10; the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 11; the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 12; and the Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 13 (collectively, the Class AA Preferred Shares).
The Series 14 Preferred Shares will be entitled to a fixed quarterly cumulative preferential dividend of [$] per share to yield [%] per annum on the issue price of $25.00. The maturity date for the Series 14 Preferred Shares will be June 30, 2030. Prior to the issuance of the Series 14 Preferred Shares, the Company will subdivide the existing Capital Shares, so that after the closing of the offering, the aggregate number of preferred shares (Class AA Preferred Shares and Junior Preferred Shares) outstanding and the aggregate number of Capital Shares outstanding will be equal. The Company has also provided notice that it will be redeeming the outstanding Class AA Preferred Shares, Series 8 on its maturity date of September 30, 2024, in accordance with its terms.
The Company’s investment objective is to hold a portfolio (the Portfolio) of Class A Limited Voting Shares of Brookfield Corporation (the BN Class A Shares; Brookfield Corporation has an Issuer Rating of “A” with a Stable trend and a credit rating on its Preferred Shares of Pfd-2 with a Stable trend by Morningstar DBRS). Brookfield Corporation was formerly known as Brookfield Asset Management Inc. (Brookfield). On December 9, 2022, Brookfield completed its public listing and distribution of a 25% interest in its asset management business, through Brookfield Asset Management Ltd. (BAM) by way of a plan arrangement. As a result of this plan arrangement, the Company received one Class A Limited Voting Share of BAM (the BAM Class A Shares, collectively with the BN Class A Shares, the Brookfield Shares) for every four BN Class A Shares it held. Currently, the Company holds 119,611,449 BN Class A Shares and 29,902,862 BAM Class A Shares. Dividends received from the Portfolio are used to fund the payment of interest on the debentures to the extent that any have been issued and to fund the payment of dividends on the Class AA Preferred Shares.
The Company has issued a limited number of Class A Voting Shares that rank senior to the Class AA Preferred Shares in respect of capital upon the dissolution, wind-up, or insolvency of the Company. There are currently 100 of such shares outstanding with a book value of USD 8,000.
Each series of Class AA Preferred Shares ranks pari passu with all other Class AA Preferred Shares and senior to:
— the Class AAA Preferred Shares,
— the Junior Preferred Shares, which currently consists of the Junior Preferred Shares, Series 1; the Junior Preferred Shares, Series 2; the Junior Preferred Shares, Series 3 and the Junior Preferred Shares, Series 4 and
— the Capital Shares,
with respect to payment of dividends and repayment of principal.
There are currently no Class AAA Preferred Shares outstanding. The Junior Preferred Shareholders are entitled to receive quarterly noncumulative cash distributions at an annual rate of 5% when declared by the board of directors. There is $321 million worth of Junior Preferred Shares currently outstanding. The Company’s Capital Shareholders will only receive excess dividend income after interest on the debentures, Class AA Preferred Share distributions, Junior Preferred Share distributions, and other Company expenses have been paid. Any capital appreciation of the Brookfield Shares will benefit the Capital Shareholders.
Following the issuance of the Series 14 Preferred Shares, the downside protection available to the Class AA Preferred Shares is expected to be approximately 91% and the dividend coverage ratio is expected to be approximately 2.7 times (x; based on the Canadian dollar and U.S. dollar exchange rate as of September 16, 2024). If the underwriters’ overallotment option is exercised, the downside protection and dividend coverage is expected to be 90.7% and 2.7x, respectively. Because of the excess-only nature of both Junior Preferred Share and Capital Share dividends, there is no grind on the Portfolio. The Company receives dividends in U.S. dollars; consequently, there is risk that an appreciating Canadian dollar will cause the dividend coverage ratio to fall below 1.0x. In the event of a shortfall, the Company may sell some of the Portfolio’s securities, engage in security lending, or write covered call options to generate sufficient income to satisfy its obligations to pay the Class AA Preferred Shares’ dividends. If the Company chooses to lend its holdings, the Portfolio would be exposed to potential losses in the event that the borrower defaults on its obligations to return the borrowed securities.
The main constraints to the credit rating are the following:
— The downside protection available to the Class AA Preferred Shareholders depends solely on the market value of the Brookfield Shares held in the Portfolio, which will fluctuate over time.
— There is a lack of diversification, as the Portfolio is entirely made up of Brookfield Shares.
— Changes in the dividend policy of Brookfield Corporation and BAM may result in reductions in the Class AA Preferred Shares’ dividend coverage.
— As the Brookfield Shares receive dividends in U.S. dollars, the Company is exposed to foreign currency risk relating to the Canadian-U.S. exchange rate, specifically the appreciation of the Canadian dollar versus the U.S. dollar. This may have a negative impact on the dividend coverage ratio of the Class AA Preferred Shares as these dividends are paid in Canadian dollars.
— Downside protection available to the Class AA Preferred Shares may be negatively affected by the retraction of the Junior Preferred Shares.
Morningstar DBRS’ credit rating on the Series 14 Preferred Shares addresses the credit risk associated with the identified financial obligations in accordance with the relevant transaction documents. The associated financial obligations are the quarterly fixed cumulative preferential dividends and the return of principal on the maturity date.
Morningstar DBRS’ credit rating does not address nonpayment risk associated with contractual payment obligations contemplated in the applicable transaction document(s) that are not financial obligations.